Portable Power Banks & Fast Chargers (GaN, Wireless, USB-C) — solving battery anxiety
1. Battery Anxiety: What It Is and Why We Feel It
“Battery anxiety” refers to the unease or stress people feel when their devices are low on power, especially when they don’t have backup power or a charger handy. In an age where smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, earbuds, portable speakers, and even laptops are essential, draining batteries threaten connectivity, productivity, entertainment, and even safety.
Reasons this anxiety persists:
- High usage: Streaming, gaming, navigation, camera use — all consume a lot of power.
- Bigger screens, more sensors, background processes — devices draw more power than before.
- More devices per person: multiple gadgets to charge.
- Varied charging availability: travel, commuting, remote areas.
- Slow chargers, low-quality accessories, bad batteries worsen the problem.
Portable power banks and fast chargers aim to mitigate this anxiety by giving quick, reliable top-ups or full charges, whether at home, in the car, or on the go.
2. Key Charging Technologies & Standards
To understand what options are good, and which are future-proof, you need to know about the technologies behind fast and portable charging.
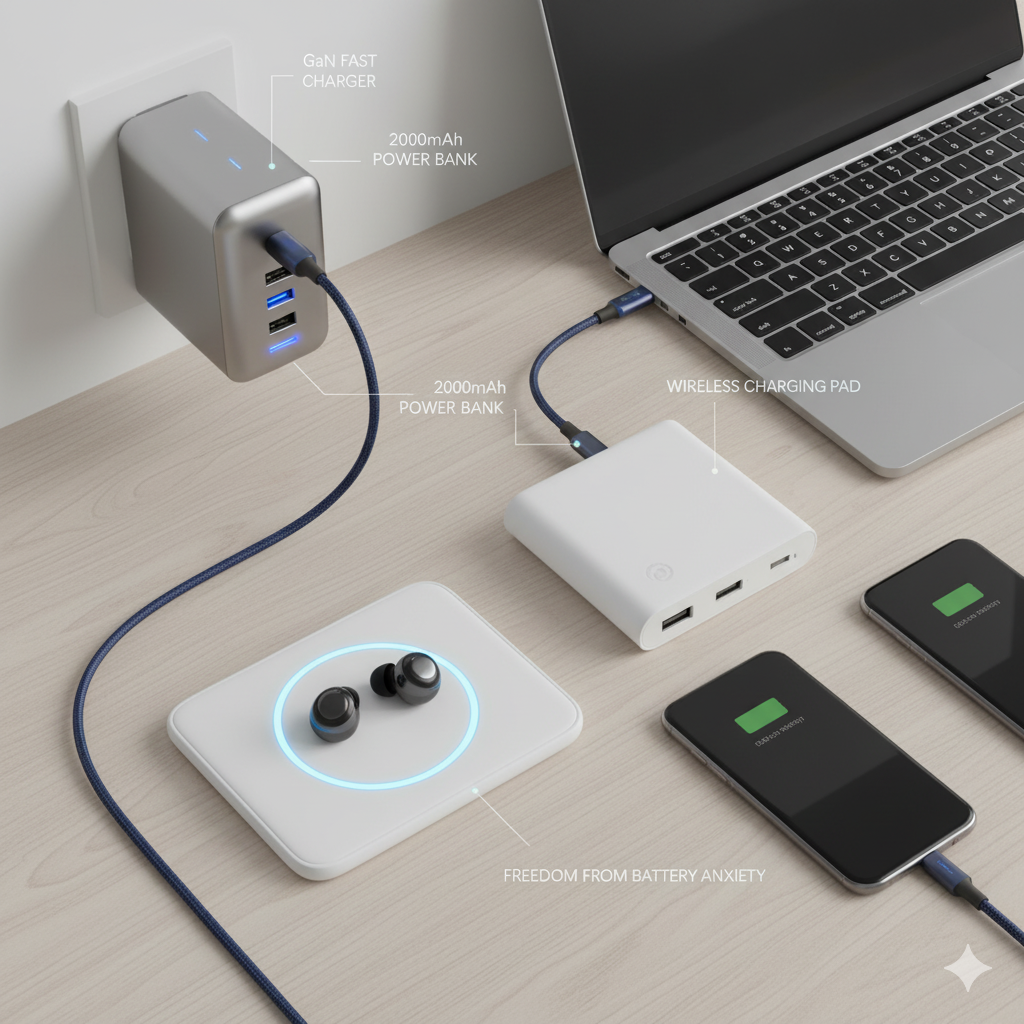
GaN (Gallium Nitride) Chargers
- GaN is a semiconductor material that allows higher efficiency, better power density, faster switching, less heat generation compared to traditional silicon. Gancharger Hub+2Business Insider+2
- Because GaN devices are more efficient and run cooler, manufacturers can build smaller, lighter chargers with high wattage capacity. HUISH+2LinTek+2
- Key advantages: compact size, less heat, ability to deliver high wattage (e.g. 65W, 100W, more), often with multiple ports. ConceptKart+2YDS Adapter+2
USB-C & USB Power Delivery (PD)
- USB-C is the connector type; PD is a standard that negotiates power delivery (voltage + current) so devices and chargers can safely draw/ provide higher wattage.
- USB PD 3.1 (latest) allows for higher wattages (often up to 240W) which is important for laptops, gaming machines, etc.
- Many devices support PD, and many chargers now implement it. Using the right cable (and correct protocol support) is essential for fast charging.
Wireless Charging & Emerging Standards
- Wireless charging uses coils and inductive (or resonant) coupling to transfer power without wires. The convenience is high, but traditionally efficiency and speed have lagged behind wired charging.
- Standards: Qi has been dominant. Newer wireless magnetic standards and magnetic alignment profiles (Qi2, magnetic power profiles) aim to improve alignment, speed, and safety. For example, wireless power banks certified to Qi2 supporting up to 25W wireless are emerging. The Verge+1
- Challenges: efficiency losses, heat, slower charging, alignment sensitivity, foreign object safety.
Fast-Charging Protocols & Proprietary Variants
- Apart from USB PD, there are proprietary fast charging protocols like Qualcomm Quick Charge, OPPO VOOC / SuperVOOC, Samsung Adaptive Fast Charging / Super Fast Charging, Xiaomi HyperCharge etc.
- These often require specific chargers / cables to achieve high wattage or very fast charge times. Knowing what your device supports matters.
- For example, in wireless standards, Qi2 enhancements are helping standardize and speed up wireless charging across brands. PC Gamer+1
3. Types of Power Banks & Fast Chargers
Understanding what types are available and their ideal niche helps you pick the right tool for battery anxiety.
Wall Adapters / Fast Chargers
- These are chargers you plug into mains outlets. Ranges from smaller chargers (20-30W) for phones to large high-wattage GaN adapters (65W, 100W, or more) capable of charging laptops.
- Multi-port chargers allow charging several devices simultaneously without needing multiple adapters.
GaN Chargers
- Because of their efficiency and size, GaN chargers are excellent for travel. They replace larger silicon bricks, especially when you need to carry chargers for phones, tablets, laptops.
- Many GaN chargers now come with multiple USB-C ports, sometimes combined with USB-A, allowing versatile device charging.
Wireless Chargers & Wireless Power Banks
- Chargers where you place your phone (or other device) on a pad, stand, or magnet dock. Very convenient; less cable fuss. Wireless power banks do the same but you can carry them.
- Wireless magnetic alignment (MagSafe, Qi2) helps secure alignment and improve charging performance.
Portable Power Banks
- These are battery packs you carry. Key metrics: capacity (mAh / Wh), number of ports, fast charging support, pass-through charging, safety, size / weight.
- Some power banks are wireless, some support high wattage USB-C PD output to charge laptops + phones; some have built-in cables or magnetic attachment.
4. Critical Features & Metrics to Watch
When evaluating power banks and chargers, these are the features that matter most.
| Feature | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Wattage / Voltage / Current / Protocols Supported | Determines how fast device charges; ensures compatibility. A charger labelled “65W PD” is more useful than generic “fast charger” if your device supports PD. |
| Number & Type of Ports | Multiple USB-C ports, USB-A for older devices; more ports means fewer separate chargers; but power sharing matters. |
| Cable & Connector Quality | Bad cables throttle speed or cause heat; cable rated wattage (e.g. 5A for high-power USB-C) matters. |
| Efficiency & Heat / Thermal Management | Less energy wasted, less heat, better for safety and battery health. GaN devices shine here. |
| Safety Features & Certifications | Over-voltage, over-current, short-circuit protection, safety certifications (UL, CE, etc.), foreign object detection in wireless chargers. |
| Size, Weight, Portability | Big for travel; bulky chargers or power banks defeat portability. |
| Battery Capacity & Charging Cycles (for power banks) | Capacity needed depending on usage; quality of battery affects how many cycles before capacity drops. |
| Wireless vs Wired Convenience vs Efficiency Trade-Off | Wired generally faster, more efficient; wireless more convenient. Balance depends on usage. |
| Future-proof / Protocol Support | Devices that support newer PD standards, wireless standards (Qi2), magnetic alignment etc., are likely to remain relevant longer. |
5. Comparing Wired vs Wireless Charging — Pros, Cons & Real-World Trade-Offs
Wired Charging
Pros:
- Generally faster and more power efficient.
- Less energy loss.
- Cooler during charge; lower heat stress on battery.
- More compatible with high wattage (for laptops, large tablets).
Cons:
- Cables are cumbersome; different connectors needed; possible wear and tear.
- Port/mounting limitations.
Wireless Charging
Pros:
- Convenience; less cable-mess; easier for quick top ups.
- More elegant for desks, nightstands, cars.
- Wireless power banks reduce cable needs on the go.
Cons:
- Slower (wired still beats wireless in speed for many devices).
- Efficiency loss (more heat, energy wasted) which can affect charging speed and may stress device / battery.
- Need good alignment (magnetic or coil alignment) to get peak performance.
- Device heat and safety concerns.
Real-World Examples
- Wireless charging standards advancing: Qi2’s move from 15W to 25W wireless helps reduce the gap. PC Gamer+1
- Wireless power banks supporting Qi2 25W already on sale. The Verge+1
6. GaN vs Traditional (Silicon) Chargers: What Makes the Difference
Here’s a deeper dive into why GaN technology is considered a big leap forward, and where its trade-offs are.
What GaN Does Better
- Size / Portability: GaN allows the design of much smaller and lighter chargers while still delivering high power. LinTek+2HUISH+2
- Efficiency: Less energy wasted as heat. Higher switching frequencies, lower on-resistance etc. Gancharger Hub+2Business Insider+2
- Thermal performance / Safety: Because less heat is generated, devices stay cooler; safer; better durability. YDS Adapter+2Anker+2
- High wattage designs: GaN enables building chargers that deliver large wattages (like 65W, 100W, 240W, and even multi-port with aggregate power) while still being pocketable.
Potential Limitations & Trade-Offs of GaN
- Cost can be higher (though prices are reducing with scale).
- Peak performance might require good cooling or ventilation; sustained full-load may still generate significant heat in smaller forms.
- Quality matters greatly — cheaper GaN chargers might cut corners on safety, certifications, quality of components.
- For lower-power devices, advantage is less noticeable.
7. Use Cases: How Different Users Solve Battery Worries
Depending on what kind of user you are, the right mix of fast charger & power bank will differ.
| User Type | What They Need | Ideal Combination of Charger / Power Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Traveler / Backpacker | Lightweight gear, minimal bulk, enough charge for phone + camera + maybe laptop; adapt to different voltages | A high-wattage GaN USB-C PD charger (multi-port) + medium-size power bank (10,000-20,000 mAh) with fast PD output; wireless backup if desired. |
| Daily Commuter | Top-ups on train/car; multiple devices (phone, buds, watch) | Wireless charger at desk/desk stand; compact power bank with wireless + wired outputs; fast charger in bag/locker. |
| Creator / Gamer | High power draw, multiple devices, heavy usage, high consumption | Big power bank with 65-100W PD or more + a powerful GaN wall charger for laptop – plus quality cables. |
| Remote/Off-Grid Use | No reliable mains; need battery backups; solar maybe; ruggedness | Large-capacity power bank(s), portable solar panels or very efficient wall / car chargers; wireless convenience optional. |
| Office / Multiple Device Household | Charging many devices at once (phones, tablets, laptops) | A powerful multi-port GaN charger; possibly charging station or hub; wireless pads for phones / watches. |
8. Current Trends & Innovations (2025)
Summarizing what’s happening now or about to happen in charging tech:
- Wireless charging standards pushing higher output: Qi2 increasing from 15W to 25W. PC Gamer
- Wireless power banks certified under Qi2 with 25W output. The Verge+1
- High-wattage GaN wall chargers / desk chargers: e.g. Ugreen’s Nexode 500W desktop charger that can power multiple devices including laptops. The Verge
- Better magnetic alignment / magnetic power profile / attachment designs to improve wireless charging efficiency.
- More compact designs and multi-port chargers to reduce number of bricks people carry.
- Focus on safety, materials, thermal profiles, certifications.
9. Risks, Limitations, & What Can Go Wrong
While fast charging and GaN & wireless tech offer big benefits, there are risks and trade-offs. Knowing them helps you choose wisely.
- Heat damage: Fast charging generates more heat, which can degrade battery health over time if not managed. Wireless especially tends to run hotter.
- Compatibility issues: Using chargers or cables that don’t support required protocols can result in slower charging or even damage. Device may limit charging if it detects incompatibility.
- Battery cycle life degradation: Very fast charging, or charging at high wattages all the time, may reduce battery lifespan.
- Safety risks: Poorly made or uncertified chargers can lead to overheating, short circuits; wireless chargers may have foreign-object vulnerabilities.
- Efficiency losses: Wireless charging especially has reduced efficiency, meaning wasted energy, more heat, slower charging relative to wired.
- Cost: High-end GaN chargers, high-capacity power banks, or certified wireless chargers can be costly.
- Size vs power trade-offs: To get very high power output, some GaN chargers still get large or heavy, especially with multiple ports.
10. Buying Guide: How to Choose What’s Best for You
Here are practical steps to pick the right power bank or fast charger for your needs so you reduce battery anxiety.
- List Your Devices and Their Charging Specs
- What devices do you own? Phones, laptops, tablet, earbuds, watch?
- Know what max charging wattage each device supports (e.g. smartphone supports 25-65W PD, laptop supports 100W PD, etc.).
- Determine Use Situations
- Where will you use the charger / power bank? Travel? At home? In the office? Outdoors?
- Decide on Wired vs Wireless Need
- If you often dock or carry cables, wireless pads are nice. But for speed and power, wired PD / fast charger is better.
- Check Protocols & Compatibility
- Select a charger that supports USB-PD and required voltage/current. If device supports PPS, QC etc., check those.
- For wireless, check standard support (Qi, Qi2, magnetic profile).
- Pick Appropriately Sized Power Bank
- Based on how many charges you need (capacity). But bigger capacity = more weight.
- Also check weight, size, built-in cables or magnetic attachments if useful.
- Consider GaN Option
- If size/weight and heat are concerns, GaN‐based charger is likely a better buy in many cases.
- Ensure Safety & Certification
- Look for recognized safety markings. User reviews of build quality, heat, durability.
- Portability & Convenience Features
- Cable management, foldable prongs, built-in displays, charge indicators, extra USB-A ports, multiple outputs.
- Budget & Value Over Time
- Sometimes spending more for a good charger/power bank gives better safety, durability, less replacement.
- After-Sales / Warranty
- Good brand support, warranty; power banks especially degrade over cycles; good brands often replace or repair.
11. Maintenance, Lifespan, and Best Practices
To make your chargers and power banks last, and maintain battery health of your devices, follow smart practices:
- Use high-quality cables (correct gauge and rated for required current).
- Avoid exposing chargers or phones to very high or very low temperatures. Heat is one of the main causes of degradation.
- Don’t leave power banks fully discharged for long periods; recharge occasionally.
- Keep wireless charging surfaces clean and ensure good alignment.
- Don’t overload a charger with too many devices beyond its rating; understand how multi-port devices share power.
- Update firmware where possible (for smart chargers / power banks with firmware).
12. The Future: Where Charging Tech is Headed
Looking forward, here are areas where charging tech is likely to evolve, helping reduce battery anxiety even further.
- Wireless charging speeds improving further — Qi2 and related magnetic standards will ramp up.
- More efficient GaN tech, possibly newer materials, even better thermal performance.
- Better battery tech in power banks: higher energy density, more charge cycles.
- Smarter chargers and banks: adaptive charging, battery health monitoring, predictive power delivery based on usage.
- Integration with renewable power / solar banking for off-grid use.
- More universal protocols: USB-PD becoming more universal; less proprietary fast charging needed.
13. Conclusion
Battery anxiety is a fact of modern digital life—but smart choices with power banks, fast chargers, GaN tech, wireless solutions make a big difference. By understanding what your devices support, choosing the right protocols, using good cables, and picking chargers built for efficiency and safety, you can significantly reduce the stress of low battery moments.
Whether you’re traveling, commuting, using multiple devices, or just want peace of mind, investing wisely in a fast charger (especially GaN) + a reliable power bank + possibly wireless top-ups gives you freedom. As charging tech keeps improving, these tools will become cheaper, more capable, more efficient — letting us worry less about power and focus more on what matters.
Share this content:













Post Comment